What is the Antenna Polarisation?
Antenna polarization holds pivotal significance during antenna selection and installation. Mismatched polarizations between transmitter and receiver antennas can lead to up to a 20 dB signal loss. Commonly, antennas employ vertical, horizontal, or circular polarizations to ensure effective communication.
Foundations of Field Equations:
Imagine an electromagnetic wave, emanating from an antenna, characterized by an electric field E (expressed as a vector) comprising two distinct components: E x and E y.
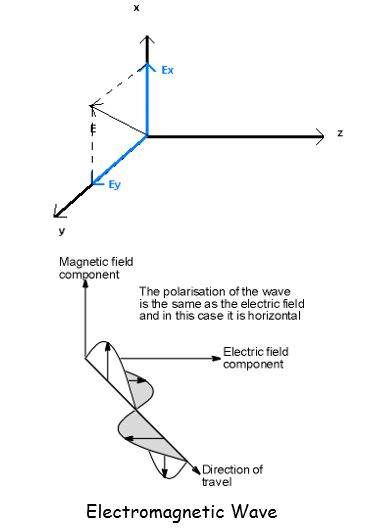
Let’s consider that the electric field E is composed of components E x and E y, and these components are represented by
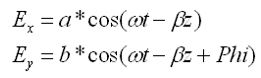
Here, a represents the amplitude of component E x, while b represents the amplitude of component E y. Phi signifies the phase difference existing between these two components.
Polarisation
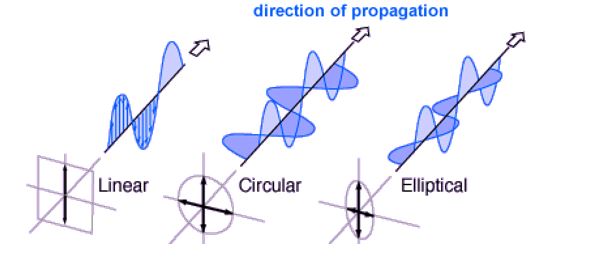
An antenna acts as a transducer, converting radio frequency electric current into electromagnetic waves that are subsequently emitted into the surrounding space. The plane of the electric field establishes the polarization or alignment of the radio wave. Generally, antennas radiate either linear or circular polarization.
In the case of a linearly polarized antenna, radiation occurs exclusively within a single plane aligned with the direction of propagation. Conversely, a circularly polarized antenna features a rotating plane of polarization, completing a full revolution during one wave period. This rotation, when clockwise in the direction of propagation, is termed right-hand circular (RHC). Conversely, when counter-clockwise, it’s referred to as left-hand circular (LHC).
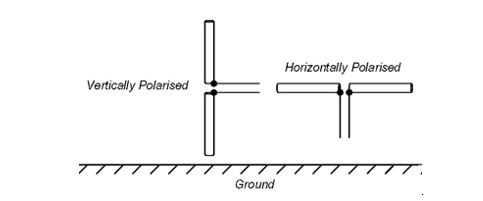
Vertical polarization (linear) characterizes an antenna when its electric field aligns perpendicularly to the Earth’s surface. A prominent example is the broadcast tower for AM radio or the “whip” antenna on vehicles. On the other hand, horizontal polarization (linear) implies that the antenna’s electric field runs parallel to the Earth’s surface. This mode is commonly employed in television transmissions.
Circularly polarized waves distribute energy across not only horizontal and vertical planes but also all planes in between. The dissimilarity between the highest and lowest peaks, as the antenna rotates through various angles, defines the axial ratio or ellipticity, often expressed in decibels (dB). An axial ratio approaching 0 dB classifies the antenna as circularly polarized, typical in cases of Helix Antennas. Conversely, an axial ratio surpassing 1-2 dB often signifies an elliptical polarization, notably when deploying crossed Yagi antennas.
What polarization is required?
The realm of communication systems predominantly gravitates towards three polarization options: vertical, horizontal, or elliptical (RHC – right-hand circular or LHC – left-hand circular). In commercial VHF/UHF applications, vertical polarization often takes precedence. Sometimes, the choice hinges on installation site considerations, directing the antenna’s orientation for optimal performance. In anticipation of this, antennas should ideally offer mounting provisions for both polarizations.
Selecting the appropriate polarization can significantly amplify overall system performance by mitigating interference from neighboring systems. For instance, aligning your system orthogonally to others in the vicinity can yield up to 20 dB of isolation, effectively reducing the interfering system’s power output by up to 99%. Furthermore, elliptical polarization has the potential to alleviate fading issues.
Numerous systems encounter challenges due to their interaction with handheld transmitters. As these devices move within environments like rooms or warehouses, the antenna’s orientation may deviate significantly from the main axis. To cater to such scenarios, fixed antennas often adopt circular or elliptical polarization, accompanied by a hemispherical radiation pattern. This configuration, while trading off high gain, ensures reasonable gain in all directions.
